Crypto lending is evolving at warp speed, and the debate between on-chain credit scores and traditional credit scores has never been more relevant. As DeFi platforms race to unlock trillions in under-collateralized loans, understanding how these two credit assessment models stack up is crucial for anyone looking to borrow, lend, or build in this space.

How Traditional Credit Scores Fit Into Crypto Lending
Traditional credit scores (think FICO or VantageScore) are built on decades of financial history: income reports, loan repayments, debt-to-income ratios, and more. These scores have long been the gatekeepers for bank loans and mortgages. In crypto lending, however, their reach is limited. Blockchain’s pseudonymous nature means users rarely share their real-world identity or financial history when interacting with decentralized protocols.
Yet, some crypto platforms are experimenting with integrating traditional credit data. For example, TransUnion now lets users share their off-chain credit information with certain crypto lenders, potentially influencing loan terms or even approval itself. But this approach comes with trade-offs: it can undermine DeFi’s promise of privacy and global accessibility.
The Rise of On-Chain Credit Scores
On-chain credit scoring is a game-changer for DeFi. Instead of relying on opaque third-party reports, these scores are generated from your blockchain activity, wallet balances, transaction history, smart contract interactions, and most importantly, your repayment record across protocols. This data is public, tamper-proof, and updates in real time as you transact.
The result? A dynamic risk profile that anyone can verify without sacrificing privacy. Platforms like Huma Finance and others are already pioneering these models to power under-collateralized loans, finally filling the missing piece in DeFi’s lending puzzle (source). If you’re a regular liquidity provider or have repaid loans on time via smart contracts, your wallet address starts to build trust, no paperwork required.
Key Differences: On-Chain vs. Traditional Credit Assessments
-

Data Sources: Traditional credit scores pull from off-chain financial data (like FICO and TransUnion reports), while on-chain credit scores analyze blockchain activity—transaction history, wallet balances, and smart contract interactions.
-
Privacy & Anonymity: On-chain credit scoring preserves user anonymity by assessing wallet addresses without requiring personal identification, unlike traditional systems that rely on sensitive personal data.
-
Accessibility: On-chain credit systems open lending opportunities to users without established financial histories, boosting financial inclusion, whereas traditional scores often exclude the unbanked or underbanked.
-
Risk Assessment: Traditional credit scores provide a broad view of a borrower’s financial behavior, including off-chain assets and liabilities. On-chain scores are transparent and tamper-proof but may miss off-chain financial risks.
-
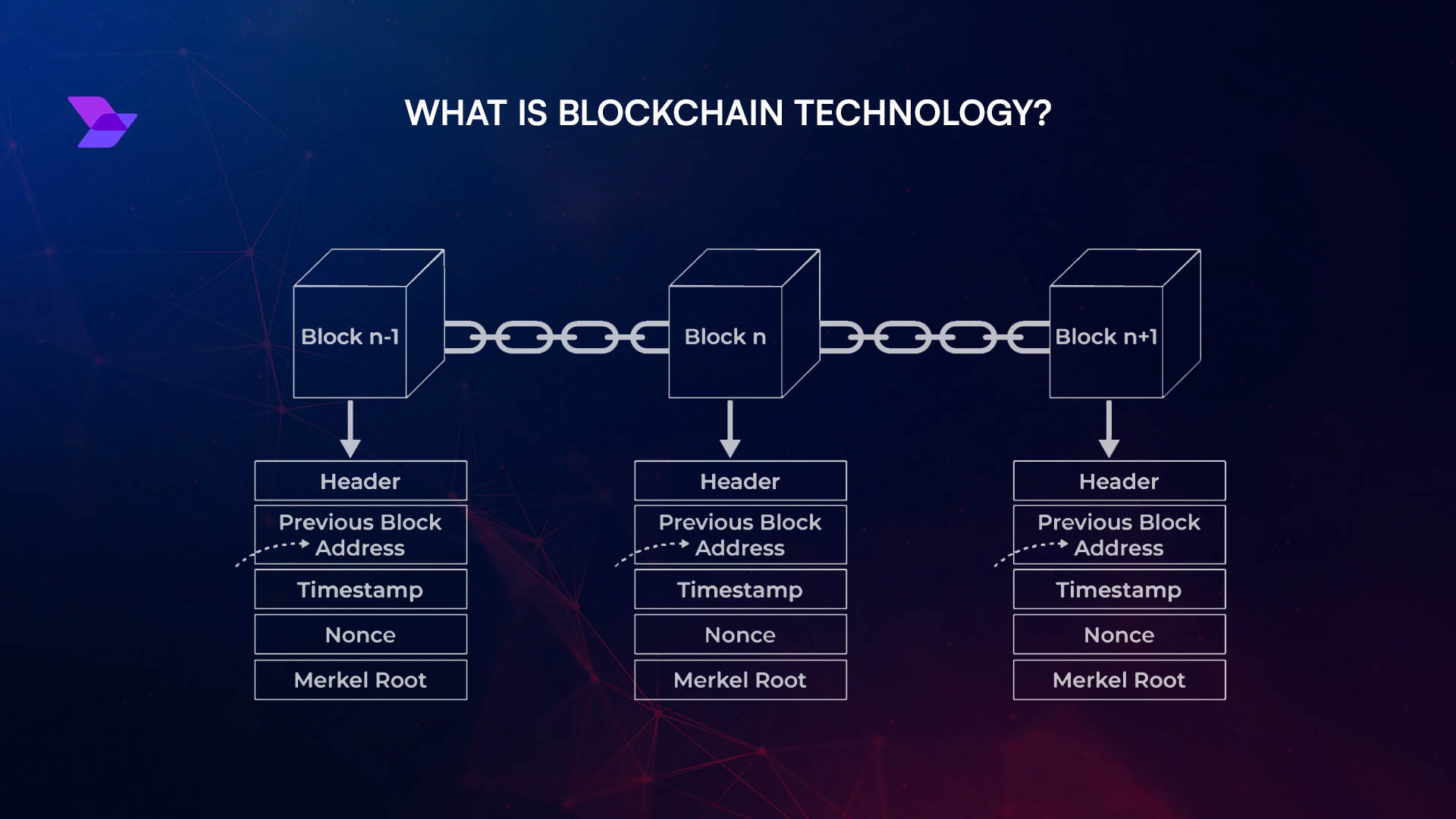
Transparency & Tamper-Resistance: On-chain credit scores are built on blockchain, making them transparent and resistant to manipulation. Traditional credit data can be subject to errors or disputes and is managed by centralized agencies.
-

Update Frequency: On-chain credit scores update dynamically as blockchain activity occurs, while traditional scores may take days or weeks to reflect changes in financial behavior.
-

Adoption in Crypto Lending: Most DeFi lending platforms (like Aave and Compound) use on-chain credit metrics or are experimenting with them, while some platforms are starting to integrate traditional credit data via partnerships with agencies like TransUnion.
Comparing Data Sources and Privacy: The Core Divide
The heart of the comparison lies in data sources. Traditional systems rely on off-chain data, from banks and employers, to create a holistic but sometimes exclusionary picture of financial health. On-chain systems flip the script by analyzing only what happens within blockchain networks: every swap, stake, or repayment becomes part of your digital reputation.
This shift has profound implications for privacy and inclusion. On-chain scoring preserves user anonymity by evaluating wallet addresses rather than personal identities (source). For millions globally who lack access to formal banking but are active in Web3 ecosystems, this opens new doors to capital without jumping through legacy hoops.
Yet, on-chain scores aren’t a silver bullet. They only capture what’s visible on the blockchain, missing out on off-chain income, debts, or real-world obligations. This can be both a strength and a weakness: while it levels the playing field and lets anyone with a wallet participate, it also means protocols must get creative with risk management and incentive structures.
Risk Assessment and Financial Inclusion in Practice
Let’s get practical. For under-collateralized loans, where borrowers put up less than the value they borrow, risk assessment is everything. Traditional credit scores are time-tested but slow to update and often exclude those without a long financial history. On-chain credit scores are instant and transparent but might not tell the full story if you’re new to DeFi or split activity across multiple wallets.
Despite these trade-offs, on-chain systems are turbocharging financial inclusion. Anyone with a positive repayment history or active participation in DeFi can build their score organically, unlocking access to capital that would be impossible in traditional finance (source). This is especially powerful in regions where banking infrastructure is weak but crypto adoption is strong.
Why On-Chain Credit Scores Are Gaining Traction
The momentum behind on-chain credit scoring isn’t just hype, it’s about solving real bottlenecks for borrowers and lenders alike. As more protocols race to offer under-collateralized loans, they need ways to separate reliable users from potential risks without sacrificing privacy or accessibility. On-chain scores provide that missing link by making trust programmable and transparent.
Here’s why this matters now:
Top Reasons DeFi Platforms Prefer On-Chain Credit Scores
-

Greater Accessibility for the Unbanked: On-chain credit scores allow anyone with a crypto wallet to access lending, regardless of their traditional credit history or geographic location. This opens up DeFi to billions of people who are underserved by conventional banks.
-

Enhanced Privacy and Anonymity: Unlike traditional credit checks that require personal identification and sensitive data, on-chain credit scoring evaluates wallet activity without revealing a user’s real-world identity—aligning with DeFi’s privacy-first ethos.
-
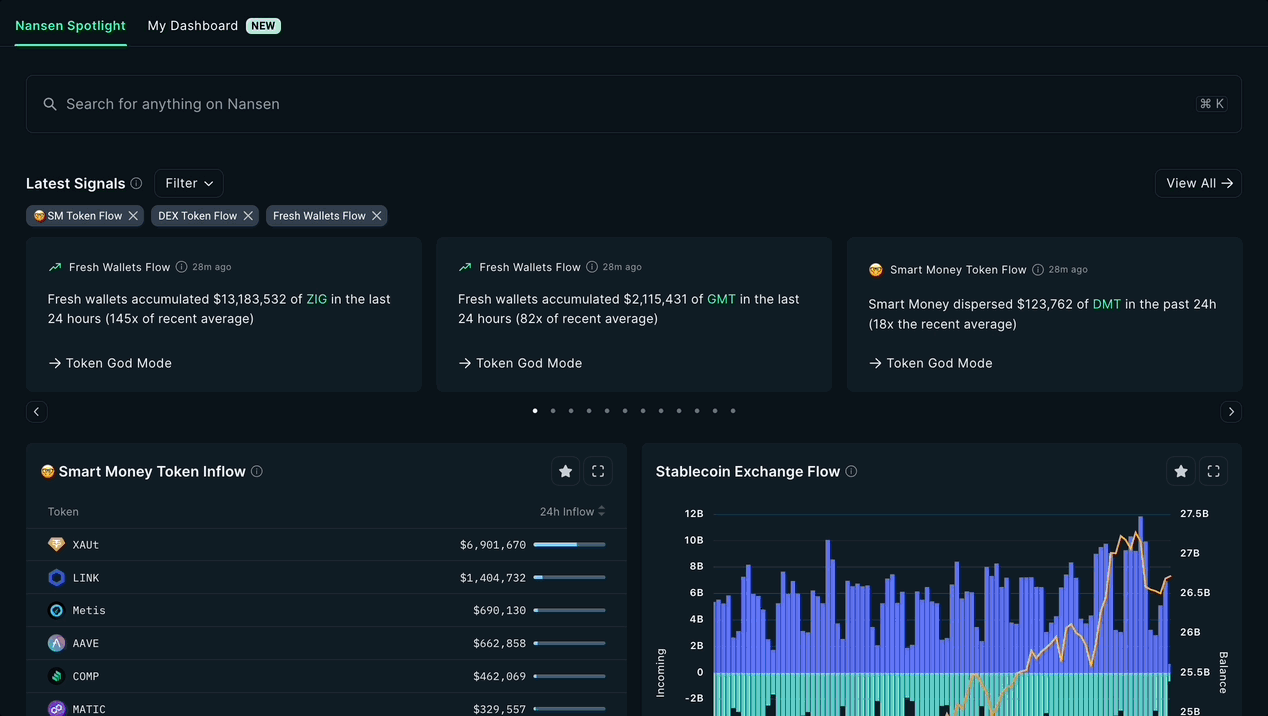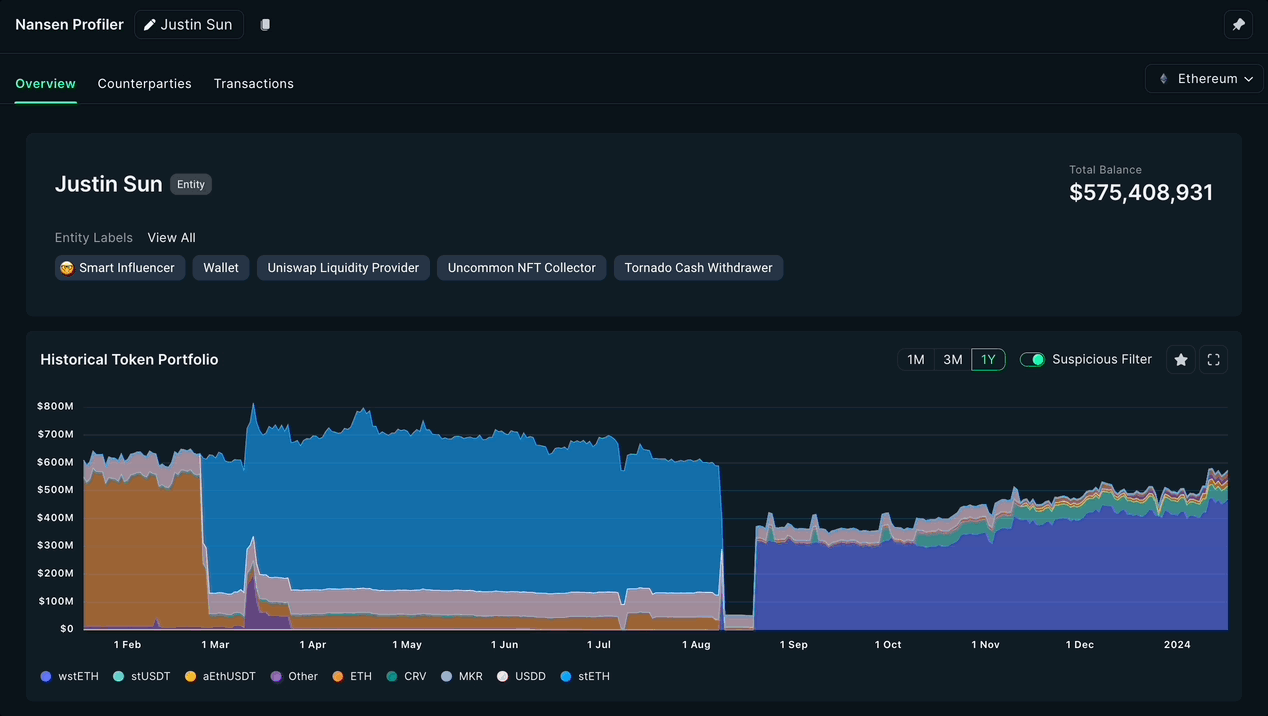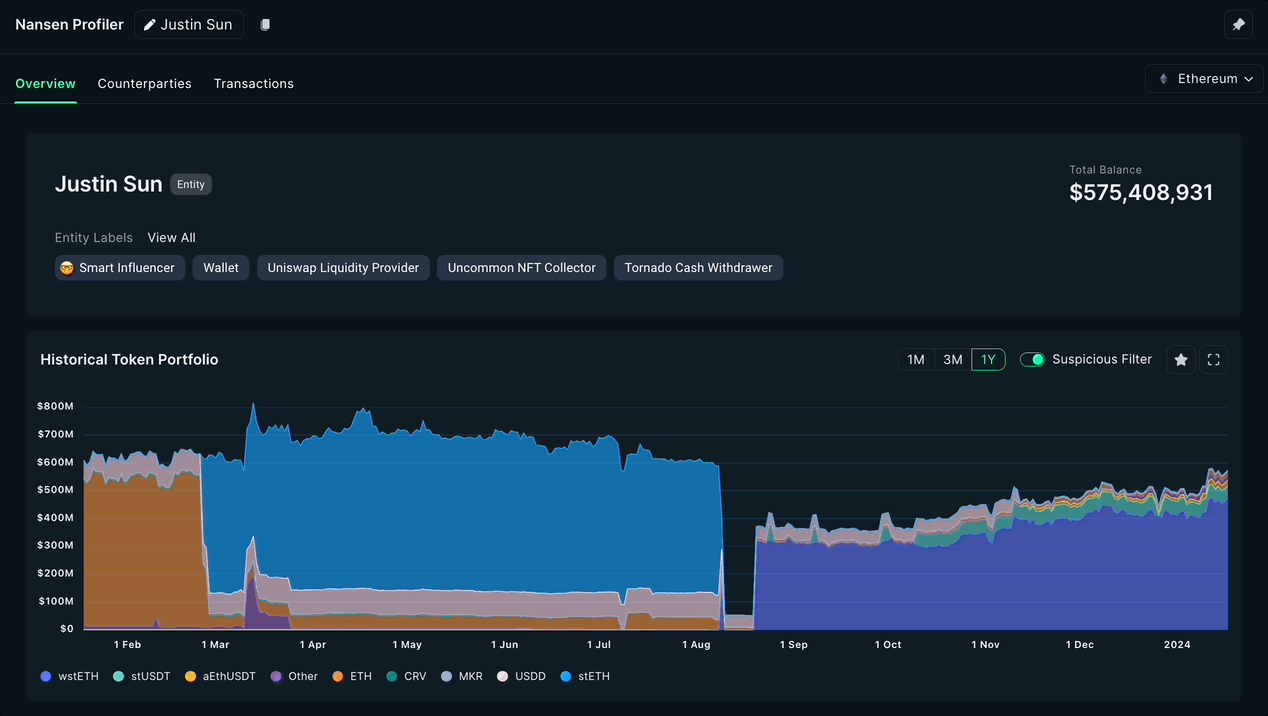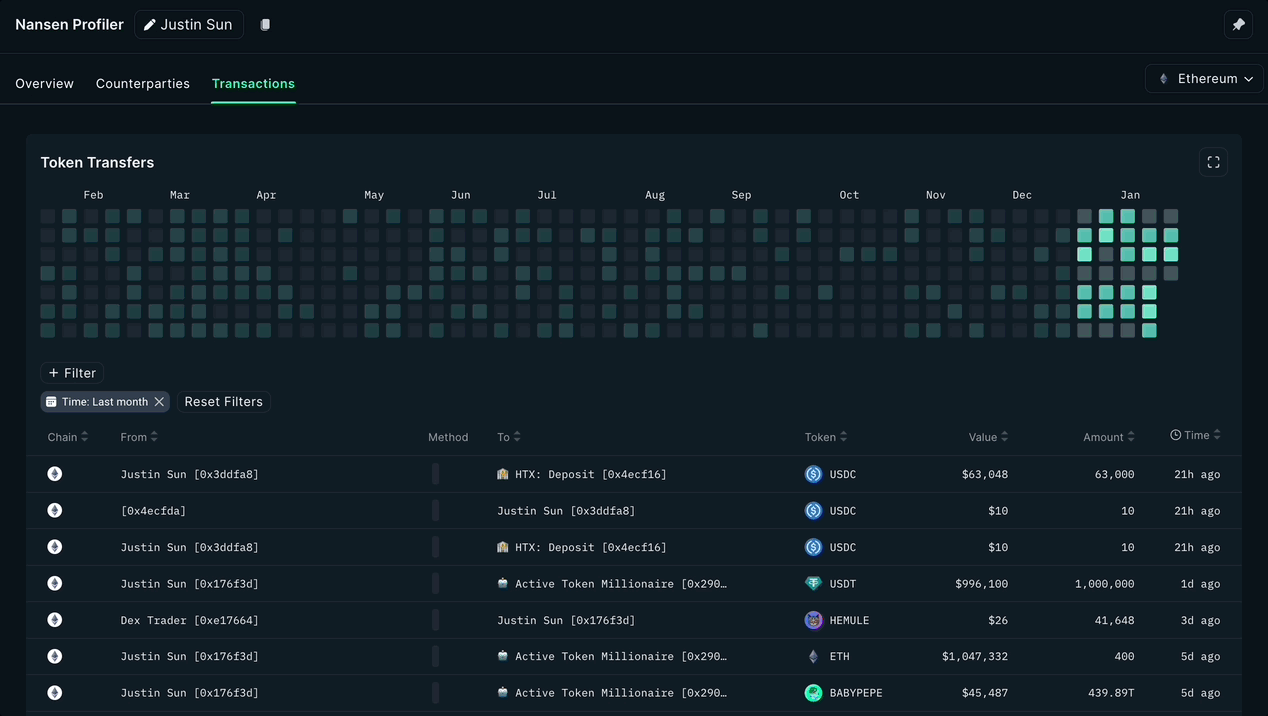
Real-Time, Transparent Credit Assessment: On-chain credit scores are constantly updated based on live blockchain activity, offering lenders up-to-the-minute insights and full transparency into a borrower’s on-chain reputation.
-
Reduced Reliance on Centralized Institutions: DeFi platforms can assess creditworthiness without involving banks or credit bureaus, removing intermediaries and streamlining the lending process through smart contracts.
-
Programmable and Interoperable Credit Data: On-chain credit scores can be integrated directly into DeFi protocols, enabling automated, composable lending products that traditional credit systems can’t match.
-

Fraud Resistance and Tamper-Proof Records: Blockchain’s immutable ledger ensures that credit histories can’t be altered or manipulated, reducing the risk of fraud compared to traditional credit reporting.
The data speaks for itself. According to recent analysis, platforms leveraging on-chain risk models are seeing increased loan volumes and lower default rates compared to early days of DeFi lending (when over-collateralization was the norm). The result? Not only do more users qualify for loans, but lenders can fine-tune their risk exposure based on verifiable blockchain behavior rather than outdated or opaque legacy data.
What Borrowers and Builders Need to Know
If you’re thinking about borrowing in crypto, or building lending products, the choice between traditional and on-chain credit scoring isn’t binary. Some hybrid models are emerging that blend off- and on-chain data for even richer risk profiles (source). But as of now, most pure-play DeFi protocols lean hard toward wallet-based scoring systems because they align better with Web3 values: transparency, permissionless access, and privacy by default.
Lenders should pay close attention to how these models evolve, especially as new standards emerge around decentralized identity (DID) and cross-protocol reputation systems. Borrowers should understand that building an on-chain track record (even small repayments or liquidity provision) can open doors previously closed by traditional gatekeepers.
Which credit scoring method do you trust more for crypto lending?
As crypto lending evolves, platforms are using both traditional credit scores (like FICO) and on-chain credit scores (based on blockchain activity) to assess borrowers. Which approach do you feel offers more trust and reliability for lending decisions?
Looking Ahead: The Future of Credit in Crypto Lending
The bottom line? The rise of the on-chain credit score marks a turning point for under-collateralized loans in crypto finance. It’s not just about disrupting legacy models, it’s about expanding access, boosting transparency, and letting your blockchain actions speak louder than paperwork ever could.
If you want to see how your own wallet stacks up, or start building your digital reputation, explore tools at cryptocreditscore. org. The next wave of lending innovation is already here… will you be part of it?






