Under-collateralized crypto lending is rapidly redefining the landscape of decentralized finance (DeFi), offering capital efficiency for borrowers and new yield opportunities for lenders. At the heart of this transformation are smart contracts, which automate and enforce loan agreements without intermediaries. As DeFi platforms evolve beyond over-collateralization, understanding the mechanics and risks of smart contracts in under-collateralized lending is essential for both participants and protocol developers.
Smart Contracts: The Automation Engine Behind DeFi Lending
Smart contracts are self-executing programs on blockchains like Ethereum, designed to automatically execute terms of a loan when predefined conditions are met. In traditional DeFi lending, these contracts take custody of collateral, calculate interest, and trigger liquidations if collateral value drops below a threshold. Over-collateralized models, where borrowers must lock up more value than they borrow, have long minimized risk for lenders but restrict broader participation.
The shift to under-collateralized crypto loans introduces new complexities. Here, borrowers provide less collateral than the loan amount or even none at all, relying instead on mechanisms such as on-chain credit scores, reputation systems, or delegated pool management. Platforms like Maple Finance and Teller Finance leverage smart contracts to assess borrower risk using transparent on-chain data rather than just asset values. This allows qualified users to access liquidity with reduced barriers while maintaining automated enforcement of repayment terms.

Automated Risk Assessment and Blockchain Loan Management
The ability to assess risk without centralized gatekeepers is a defining feature of DeFi smart contract applications. Automated risk assessment uses blockchain data, such as historical repayment records or wallet activity, to calculate trust scores for borrowers. These scores are then encoded into smart contract logic that determines loan eligibility and terms in real time.
This approach enables near-instant loan approvals and disbursements while reducing human bias and manual processing errors. For example, when a borrower requests an under-collateralized loan, the smart contract can instantly pull their on-chain credit score, verify eligibility against protocol rules, and release funds if criteria are met, all without exposing lenders to unnecessary counterparty risk.
Security Protocols: Mitigating Smart Contract Risks
Despite their transparency and automation benefits, smart contracts introduce unique attack surfaces in DeFi lending protocols. Under-collateralization amplifies these risks since lenders have less protection if a borrower defaults or exploits a contract vulnerability.
To address this, leading platforms implement robust security measures such as multi-oracle price feeds (for accurate asset valuations), emergency pause functions (to halt suspicious activity), and transparent governance frameworks that allow community oversight. For instance, Maple Finance employs both automated payment routing through smart-contract escrow and delegated pool managers who vet borrowers before loans are issued (source). These layered controls help shrink resolution timelines from months to minutes compared to traditional finance.
Top Security Features in Under-Collateralized DeFi Lending
-
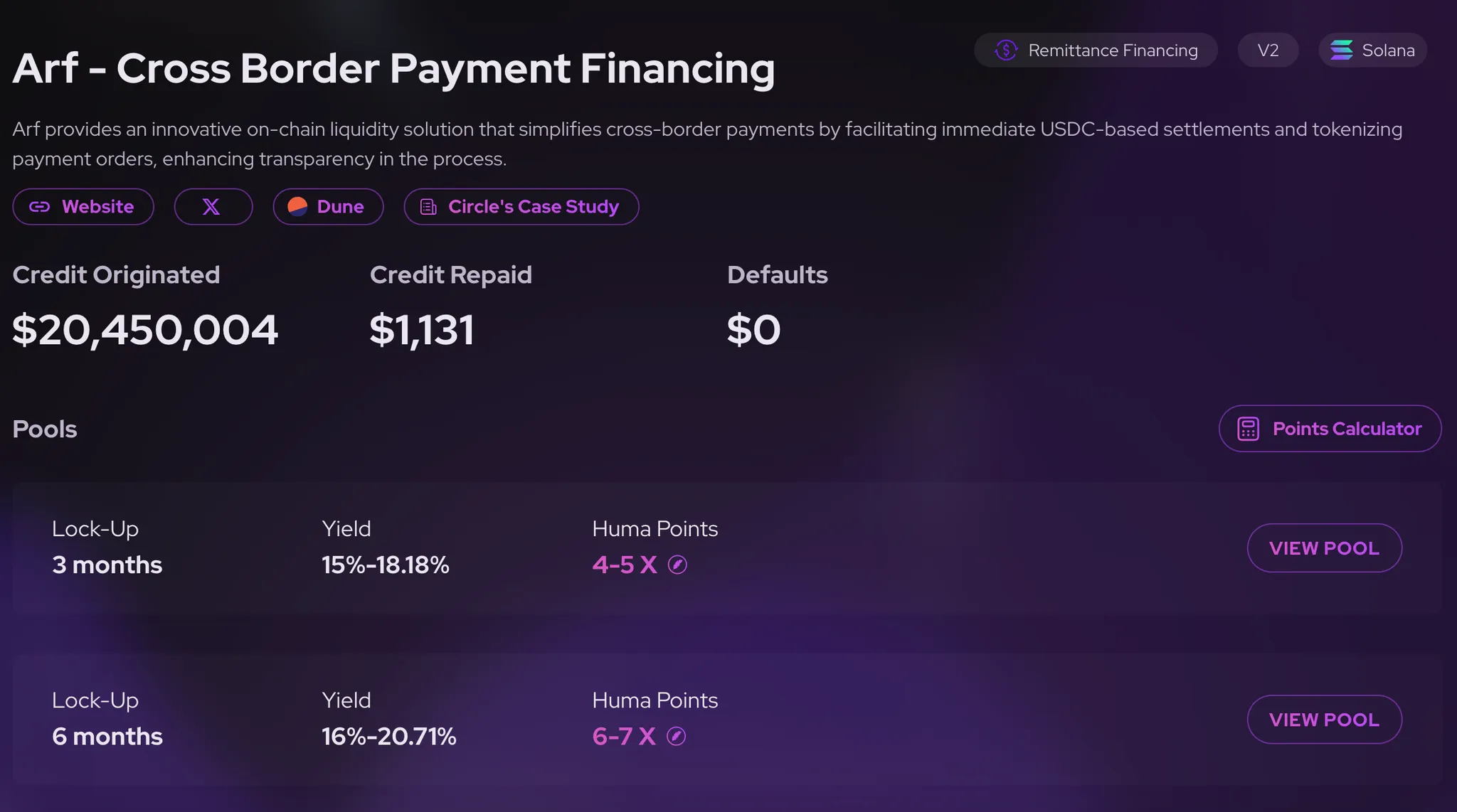
Multi-Oracle Price Feeds: Platforms like Maple Finance utilize multiple independent oracles to aggregate asset prices, minimizing manipulation risk and ensuring accurate collateral valuation.
-

Automated Smart Contract Audits: Leading protocols such as Teller Finance undergo regular third-party smart contract audits to identify vulnerabilities and enhance code security.
-

Emergency Pause Functions: Many DeFi lending platforms implement emergency pause or circuit breaker mechanisms, allowing administrators to halt protocol operations in response to suspicious activity or exploits.
-

Transparent On-Chain Governance: Protocols like Aave employ decentralized governance frameworks, enabling token holders to vote on risk parameters and security upgrades in a transparent manner.
-

Reputation-Based Borrower Assessment: Under-collateralized lending platforms such as Maple Finance and Teller Finance leverage on-chain credit scoring and reputation systems to evaluate borrower trustworthiness, reducing default risk.
The interplay between automation and security will continue to define the success of under-collateralized crypto lending as adoption grows across global markets.
As the space matures, blockchain loan management is evolving to balance capital efficiency with risk mitigation. Protocols are increasingly integrating advanced analytics, decentralized identity solutions, and real-time monitoring to refine borrower assessment and protect lender capital. For example, some platforms now use multi-factor on-chain risk models that incorporate wallet age, transaction diversity, and repayment consistency, creating a more nuanced picture of borrower reliability than static collateral ratios alone can provide.
Emerging protocols are also experimenting with hybrid approaches, combining smart contract automation with off-chain data sources or legal recourse for institutional-grade lending. This hybridization aims to attract traditional financial institutions while preserving the core benefits of DeFi: transparency, programmability, and open access.
Opportunities and Challenges Ahead
The rapid uptake of under-collateralized crypto loans is reshaping how both individuals and institutions interact with digital assets. By reducing the collateral barrier, these products expand credit access to users previously excluded from DeFi lending markets. Lenders benefit from higher yield opportunities, albeit with elevated risk profiles that demand robust due diligence and dynamic monitoring.
However, this evolution is not without challenges. Smart contract vulnerabilities, oracle manipulation attacks, and flash loan exploits are persistent threats in DeFi. The complexity of under-collateralized lending amplifies these risks since default events can have cascading effects across interconnected liquidity pools. As such, ongoing security audits, bug bounty programs, and transparent governance processes are non-negotiable for platform resilience.
Moreover, the regulatory environment remains fluid. As regulators scrutinize DeFi lending practices, particularly those involving minimal collateral, protocols must adapt quickly to new compliance standards without compromising decentralization or user privacy.
The Future of Smart Contracts in Decentralized Credit Markets
The next phase for smart contracts in under-collateralized lending will likely center on interoperability between blockchains, composability with other DeFi primitives (such as insurance or derivatives), and enhanced user protections via programmable risk controls. With advances in decentralized identity (DID) frameworks and on-chain reputation systems, smart contracts can facilitate even more granular credit scoring, enabling broader adoption while minimizing systemic risk.
For users: Engaging with these platforms requires an understanding of both the technical mechanics (e. g. , how automated liquidations work) and the associated risks (e. g. , potential for contract exploits). Leveraging tools that provide transparent on-chain credit scores or real-time protocol health metrics is increasingly essential for informed decision-making.
The synergy between automated risk assessment and blockchain loan management is unlocking unprecedented financial flexibility, but only for those prepared to navigate its complexities responsibly. For developers and protocol designers, continuous innovation around security controls and transparency standards will be pivotal as competition intensifies across global markets.






