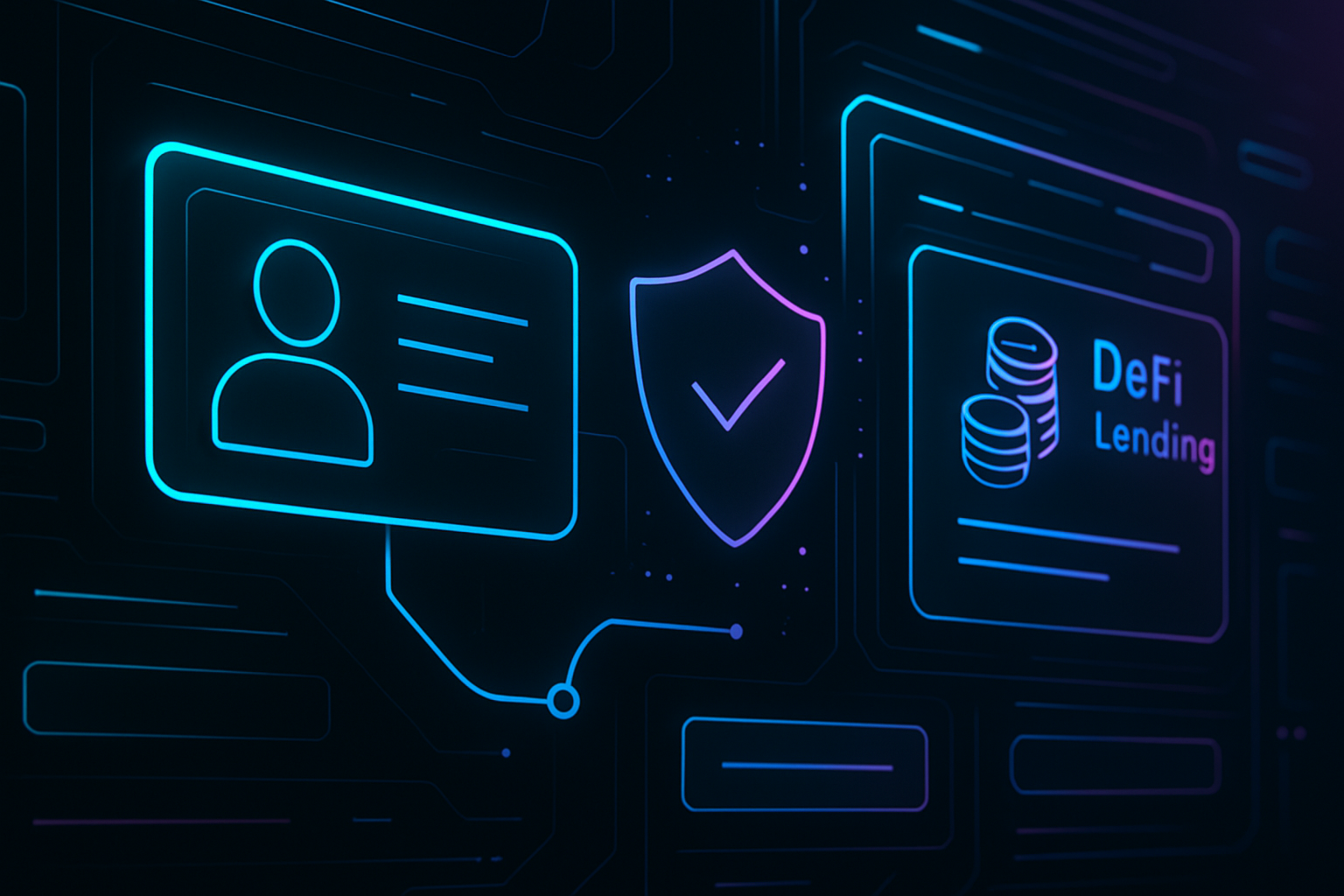
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has revolutionized access to financial services, but its earliest lending protocols relied heavily on over-collateralization. This model, while minimizing default risk, creates steep barriers for would-be borrowers lacking substantial crypto assets. In 2025, the convergence of decentralized identity for DeFi lending and on-chain risk score crypto solutions marks a pivotal shift, enabling under-collateralized lending at scale and unlocking new opportunities for both users and capital allocators.

DID: The Foundation for Trust in a Pseudonymous World
The challenge of trust is central to blockchain-based lending. Traditional finance leans on government-issued identities and credit bureaus; DeFi operates with wallet addresses that are pseudonymous by design. Decentralized Identity (DID) bridges this gap by empowering users to create self-sovereign digital identities. These DIDs allow individuals to selectively disclose verifiable credentials, such as proof of address or KYC status, without surrendering control to a centralized authority.
This self-managed identity paradigm is more than a technical upgrade; it’s an ideological shift toward privacy-preserving transparency. Borrowers can build reputational capital on-chain, while lenders gain confidence through cryptographically-secured attestations. As adoption grows, DID in crypto finance will serve as the backbone for scalable credit assessment frameworks.
On-Chain Risk Scores: Quantifying Creditworthiness Without Borders
Traditional credit scoring models are opaque, siloed, and slow to adapt. In contrast, onchain credit scoring DeFi protocols operate transparently and leverage real-time blockchain data. By analyzing wallet activity, transaction volumes, repayment patterns, protocol interactions, these systems generate dynamic risk scores that reflect a borrower’s true behavior across the ecosystem.
The On-Chain Credit Risk Score (OCCR Score), for example, evaluates liquidation probabilities using historical and live data feeds. Protocols like RociFi take this further by issuing Non-Fungible Credit Scores (NFCS), segmenting borrowers into risk tiers that directly inform loan-to-value ratios and interest rates. This approach not only reduces information asymmetry but also automates much of the underwriting process previously handled by centralized institutions.
Key Benefits of On-Chain Risk Scores in DeFi Lending
-
Improved Capital Efficiency: On-chain risk scores enable under-collateralized lending, allowing borrowers to access loans with less collateral. This increases the overall utilization of capital compared to traditional over-collateralized DeFi models.
-

Broader Financial Inclusion: By leveraging Decentralized Identity (DID) and transparent credit assessment, on-chain risk scores help users without significant crypto assets to participate in DeFi lending markets, expanding access to financial services.
-
Dynamic Loan Terms: On-chain risk scores allow for personalized loan-to-value ratios and interest rates based on a borrower’s risk profile, optimizing terms for both lenders and borrowers.
-
Enhanced Fraud Prevention: Combining DID with on-chain analytics strengthens identity verification and reduces the risk of Sybil attacks and identity fraud in decentralized lending protocols.
-

Greater Transparency and Trust: All risk assessments are conducted on-chain, ensuring verifiable and tamper-proof credit scoring that builds trust between borrowers and lenders without centralized intermediaries.
Unlocking Under-Collateralized Lending: New Frontiers in Capital Efficiency
The integration of DID systems with robust on-chain risk scores is already reshaping under-collateralized lending blockchain protocols. Instead of requiring borrowers to lock up more collateral than they borrow, a practice that undermines financial inclusion, platforms can now assess individual borrower risk with unprecedented precision.
This innovation drives greater capital efficiency across money markets while broadening access for users who previously lacked sufficient assets to participate. Lenders benefit from improved yield opportunities as protocols diversify their borrower base without blindly increasing exposure to default risk.
However, this evolution introduces new challenges around data privacy, sybil resistance (preventing fake identities), and adoption incentives. Protocols must balance transparency with user confidentiality while building mechanisms to verify decentralized identities at scale, a nuanced problem explored further at /how-decentralized-identity-did-and-onchain-risk-scores-enable-under-collateralized-defi-lending.
Another critical dimension is the ongoing refinement of risk models. Unlike static credit checks in traditional finance, on-chain risk scores are inherently adaptive. As borrowers interact with multiple protocols and demonstrate repayment discipline, their scores evolve in real time, potentially lowering borrowing costs and increasing access to larger loans. This dynamic feedback loop incentivizes positive financial behavior and aligns the interests of lenders and borrowers more closely than ever before.
Protocols such as Credora, Spectra, and Cred are at the forefront of this movement, combining DID frameworks with sophisticated analytics to create a transparent underwriting process. These platforms leverage smart contracts to enforce loan terms autonomously, reducing operational overhead and minimizing human bias from lending decisions. The result is a more inclusive ecosystem where users across the globe can access liquidity based on merit rather than connections or geography.
Navigating Risks: Privacy, Security, and Adoption Barriers
Despite these advancements, several risks remain at the intersection of decentralized identity for DeFi lending and under-collateralized lending blockchain solutions. Privacy remains paramount, protocols must safeguard user data while maintaining enough transparency for effective risk assessment. Techniques like zero-knowledge proofs are increasingly being adopted to allow verification without revealing sensitive information.
Sybil attacks, where malicious actors create multiple fake identities to exploit protocols, pose another challenge. Effective DID systems must incorporate robust verification mechanisms without sacrificing user experience or accessibility. Additionally, widespread adoption depends on interoperability standards that enable seamless identity usage across diverse DeFi platforms.
Key Challenges for Under-Collateralized DeFi Lending with DID & On-Chain Risk Scores
-

Data Privacy and Security Concerns: While Decentralized Identity (DID) systems empower users to control their data, ensuring privacy and protection of sensitive identity information on public blockchains remains a major challenge. Protocols must balance transparency with robust encryption and privacy-preserving technologies such as zero-knowledge proofs.
-
Identity Fraud and Sybil Attacks: The pseudonymous nature of DeFi exposes platforms to risks of fake or duplicate identities (Sybil attacks), which can undermine the reliability of on-chain risk scores and lead to untrustworthy lending environments. Solutions like Chainlink DECO are being explored to verify identities securely.
-

Limited Adoption and Interoperability: DID standards and on-chain risk scoring protocols are still emerging, leading to fragmentation and limited cross-platform compatibility. Achieving widespread adoption requires interoperable solutions that can function seamlessly across multiple DeFi platforms and blockchains.
-

Accuracy and Reliability of On-Chain Risk Scores: On-chain credit scores, such as those from RociFi or OCCR Score, rely on historical blockchain data, which may not capture off-chain behaviors or nuanced credit risks. This can result in incomplete risk assessments and potential loan defaults.
-

Regulatory Uncertainty and Compliance: The evolving regulatory landscape for DeFi and digital identity introduces uncertainty regarding KYC/AML requirements. Platforms must navigate global compliance challenges without compromising decentralization, as highlighted in the U.S. Treasury’s DeFi risk assessment.
-

Capital Efficiency vs. Risk Management: While under-collateralized lending increases capital efficiency, it also heightens the risk of defaults and protocol losses. Striking the right balance between accessible lending and effective risk controls is a persistent challenge for DeFi protocols.
The Road Ahead: Toward Trillions in On-Chain Credit
The momentum behind onchain credit scoring DeFi is unmistakable. As more protocols implement these tools, we can anticipate a dramatic increase in both the volume and diversity of participants in decentralized lending markets. Analysts project that unlocking even a fraction of global credit demand through under-collateralized crypto loans could bring trillions of dollars into DeFi within the next decade.
This transformation will not be instantaneous or without friction; it will require disciplined governance, continuous technical innovation, and thoughtful regulation that respects both privacy and financial integrity. Yet the direction is clear: DID in crypto finance combined with transparent risk modeling is setting new benchmarks for trustless lending globally.
For developers, lenders, and borrowers seeking actionable insights or integration support for these emerging standards, further resources are available at /how-decentralized-identity-did-and-onchain-risk-scores-enable-under-collateralized-defi-lending. The future of decentralized credit will be shaped by those who understand, and responsibly harness, the power of data-driven trust.







